Our Solar System
Solar System:
Consists of all the planets that orbits a Star (ex our Sun). In addition to planets, the Solar System also consists of moons, comets, asteroids, minor planets, and dust and gas.
Our sun
Sol:
The name of our Sun which is technically a star. Hence why it is called Sol-ar System.
Star:
Stars are the only objects in the universe that create light, this is done through the release of energy produced by nuclear reactions at its core.
Temperature of our sun is about 15 million degrees celsius!
Magnitude:
Brightness of stars is assigned a number starting with the brightest star starting at about -1 magnitude. The brighter the star the hotter the star!
Aurora Borealis and The Sun
- The sun is a massive hot atomic cooker, constantly exploding and fusing atoms to create heavier atoms. From time to time the Sun releases ionized gas (particles that have a charge), this is called a Solar Flare.
Never observe the sun with the naked eye!
- Never ever observe the sun with your naked eye, it may lead to permanent eye damage!
- You must wear polarized sunglasses that block out harmful rays that may burn out your retina.
Space is big, duh!
DISTANCE OF EARTH FROM THE SUN
Astronomical unit (Au):
The distance from Earth to the Sun, roughly about 150,000,000 km
A light year:
The distance light travels in one year, roughly about 9.5 Trillion km.
Gravity
Gravitational force:
Is a force that attracts any object with mass (an object must have a lot of mass to notice that gravitational pull)
Planetary sizes
Poster Project
Using construction paper create a poster similar to the one depicted here:
Make sure to have a proper scale, for example:
- notice 2 Mars' can fit side by side into Earth
- Uranus is about 4 Earth's wide
- Saturn is as a bit wider a than Uranus and Neptune put side by side
- Jupiter is a Saturn plus 3 Earths wide
Start with your smallest planets and then work up from there.
Earthly Terms
Equator:
An imaginary line on the Earth's surface equal distance from the North Pole and South Pole.
Northern Hemisphere:
The half of the Earth that is North of the equator
Southern Hemisphere:
The half of the Earth that is South of the equator
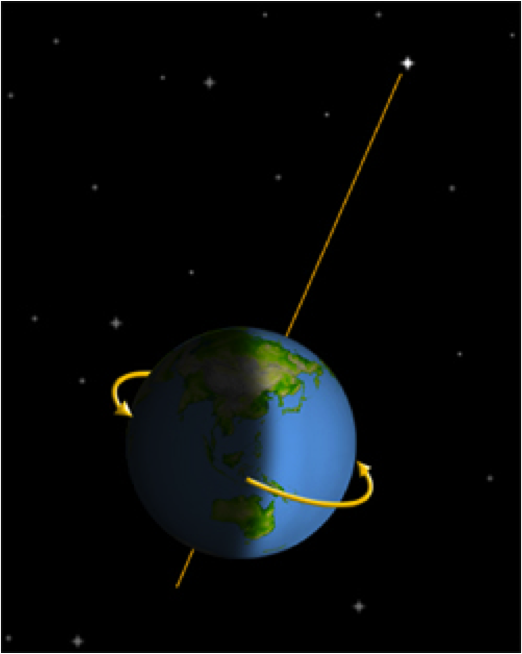
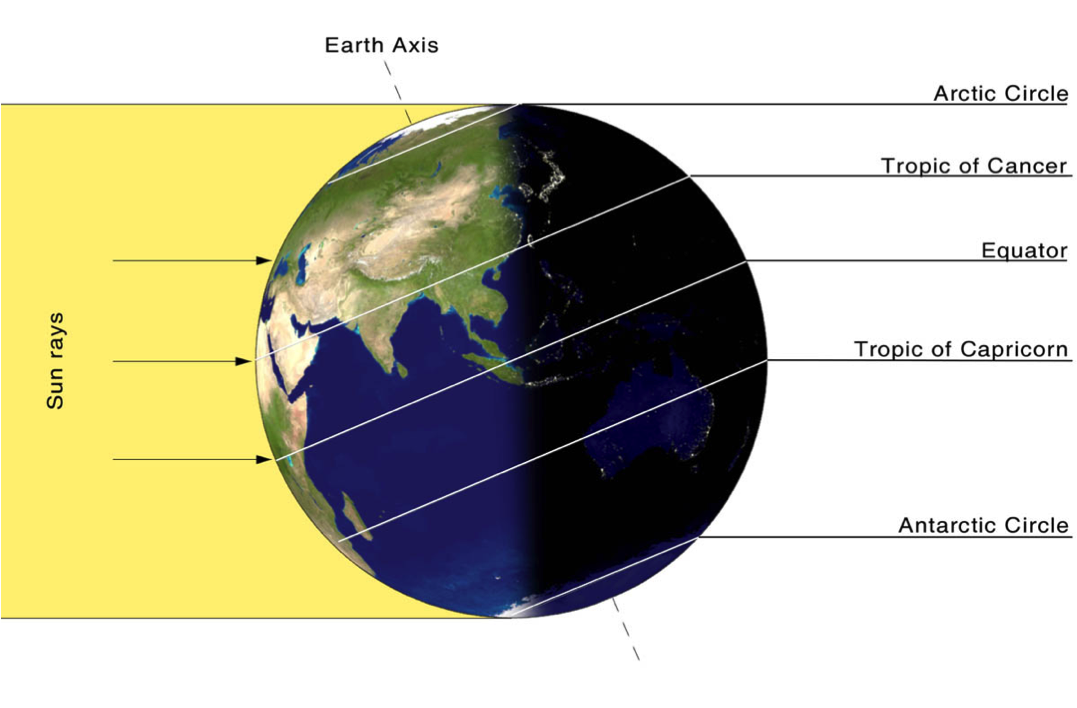
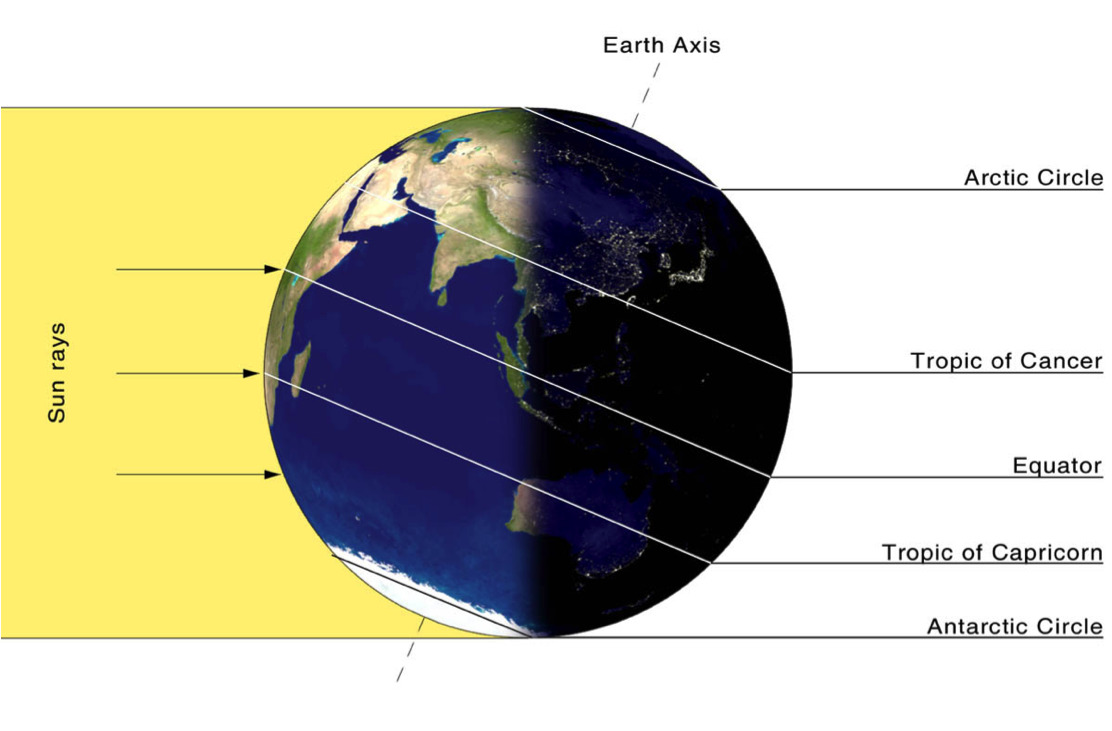
Earth's Axis:
The axis of the Earth is an imaginary line drawn through the North Pole and the South Pole. Earth spins around this axis.
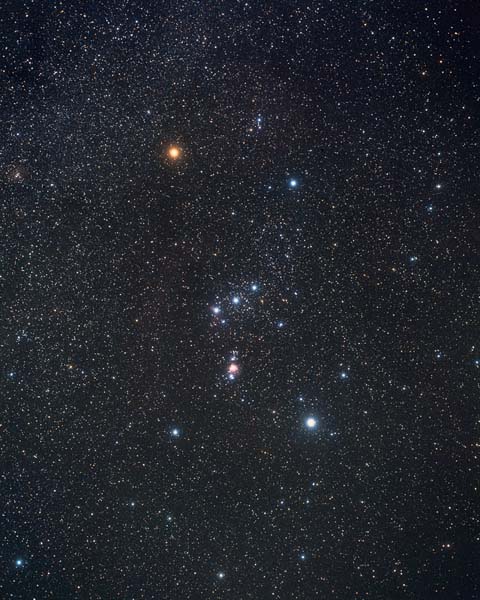
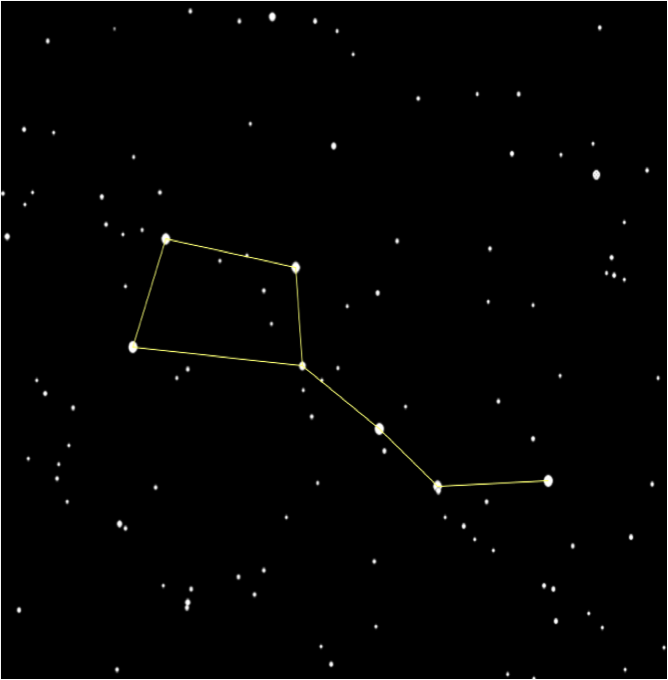
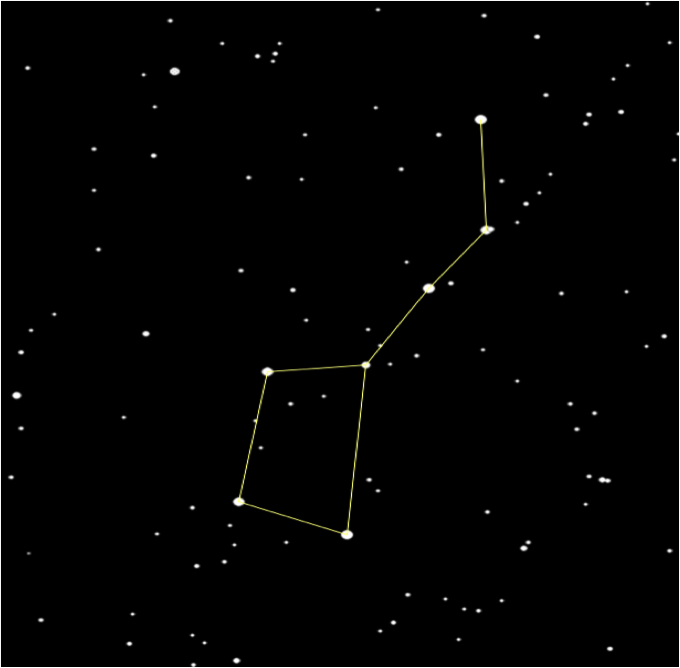
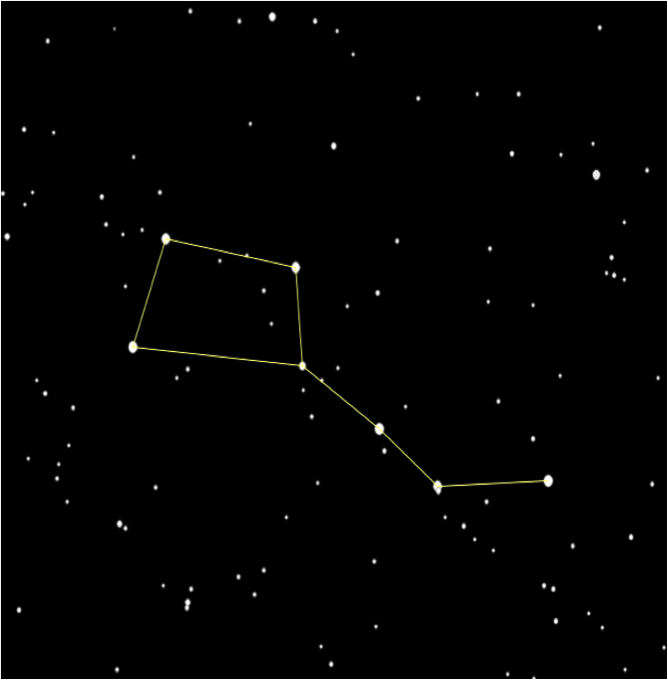
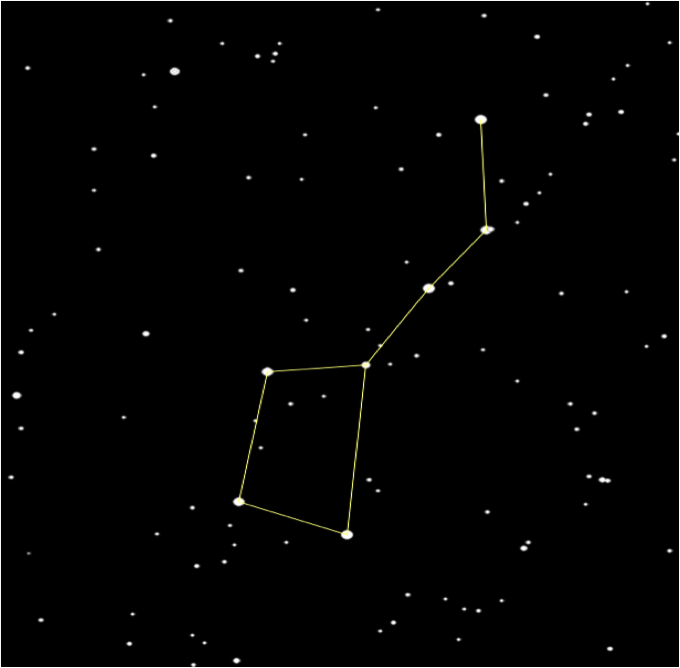
Constellations
What do you think are constellations?
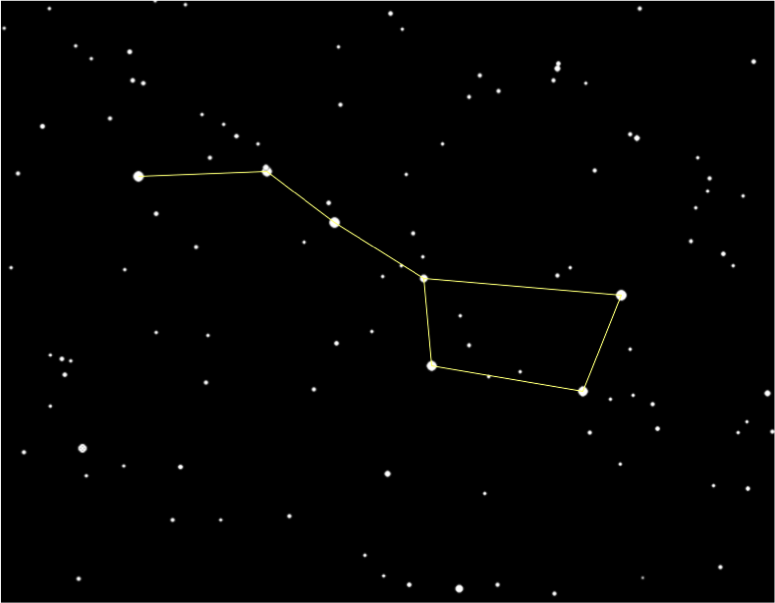
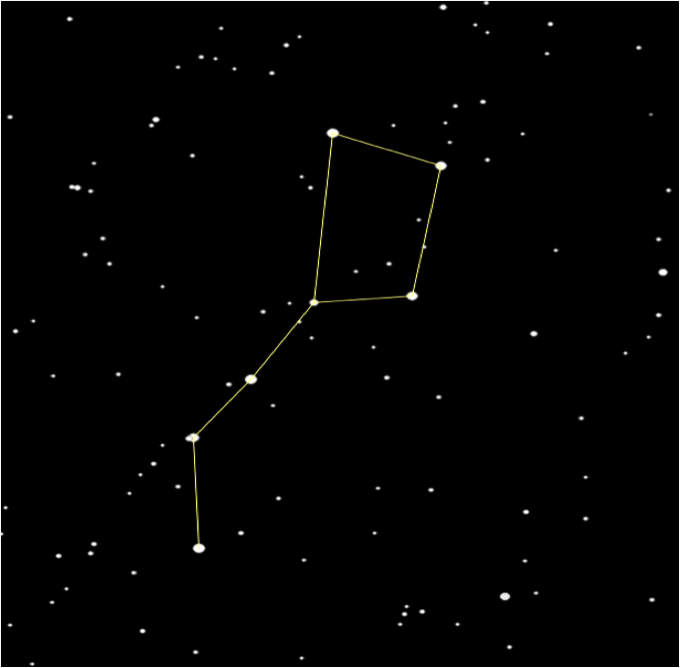
Constellation:
A constellation is a group of stars, usually in a recognizable shape or pattern. Together, the stars look like a picture. The word constellation comes from Latin: con-, meaning together and stella- meaning stars.
In ancient Egypt, the observation of stars such as Sirius in the day and night sky were used from a very ancient period, in order to predict the Nile Flood
Some Popular Constellations
Some constellations that can be easily noticed in the night sky of the Northern Hemisphere are:
- Ursa major (The Great Bear) - Also known as the big dipper
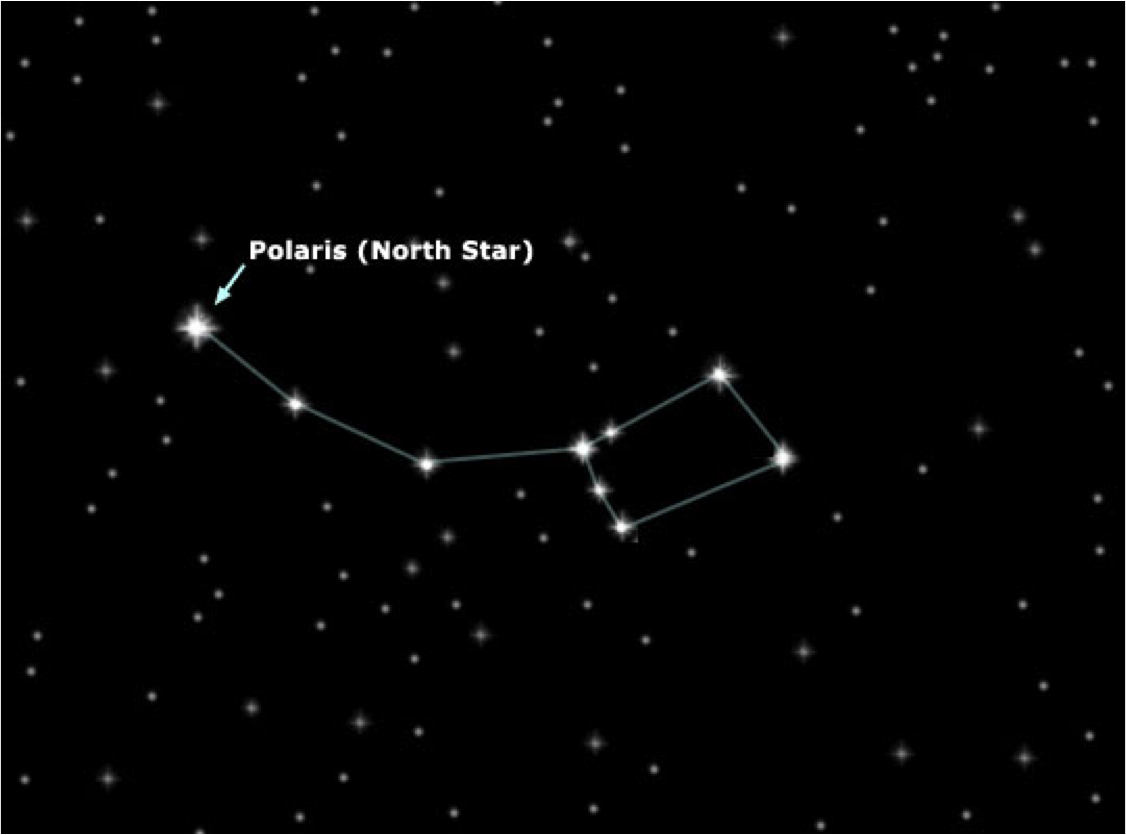
- Ursa Minor (The Little Bear) - The last star in Ursa Minor's tail (or the last star on the handle of the little dipper) is the north star Polaris.
- Orion (Orion has a belt)
You're Lost in the woods? Look up!
Polaris:
Considered to be the 'North Star' this star does not move across the night sky because of its position right above Earth's northern axis.
In a time-lapse photo all the streaks are stars moving across the night sky, the one star that is not a streak (rather it's a dot) is the star Polaris, it barely moves across the night sky because it is above the north pole.
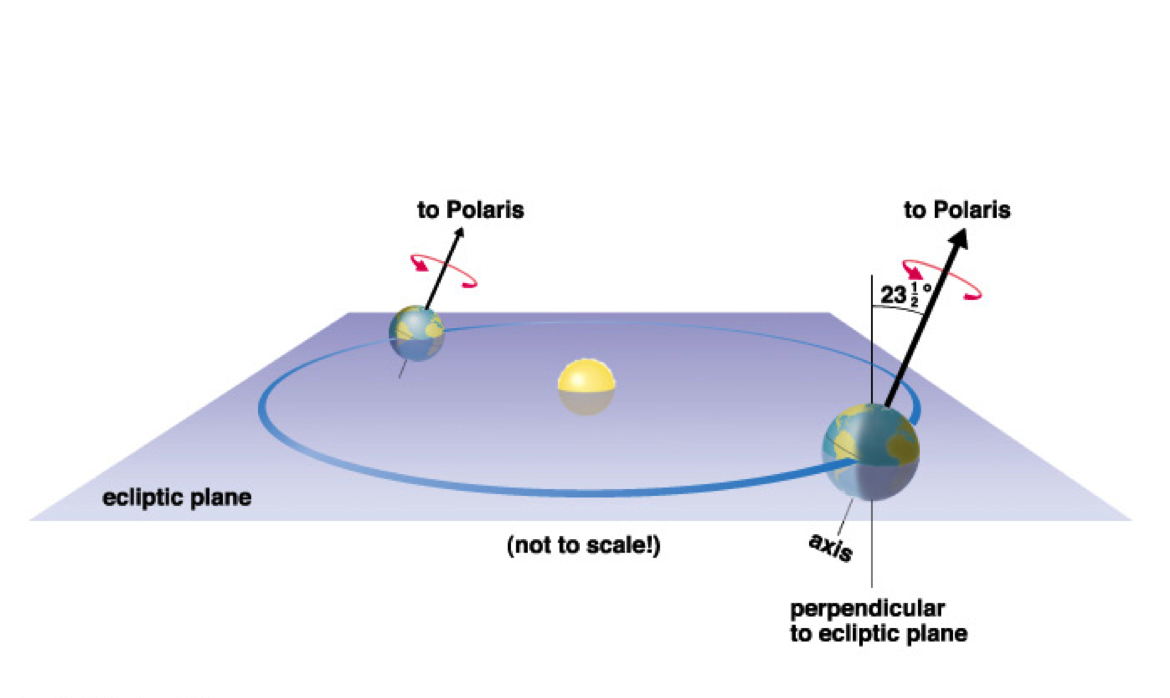
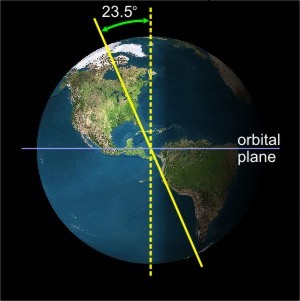
The Earth's Tilt
The Earth is tilted by 23.5 degrees, this attributes to:
- The changes in seasons
- The amount of daylight Earth receives during the seasons
- Why the Sun appears to be lower in the sky in winter compared to summer.
Seasonal Changes
The seasons throughout the year change due to how much direct sunlight each hemisphere receives when the Earth changes its position in its orbit around the sun.
- Greater amounts of direct sunlight means warmer temperatures
- Greater amounts of daylight also means warmer temperatures
- Whichever hemisphere (or pole) that is leaning towards the sun is the hemisphere that will be experiencing Summer.
- Whichever hemisphere (or pole) that is leaning away from the sun is the hemisphere that will be experiencing Winter.
Sunset & Sunrise
During winter months the days are short and nights are long
- The sun rises later
- The sun sets earlier
During summer months the days are long and nights are short
- The sun rises early
- The sun sets late
The sun's position over the seasons
- During the winter months the sun appears lower in the sky
- During the summer months the sun appears higher up in sky
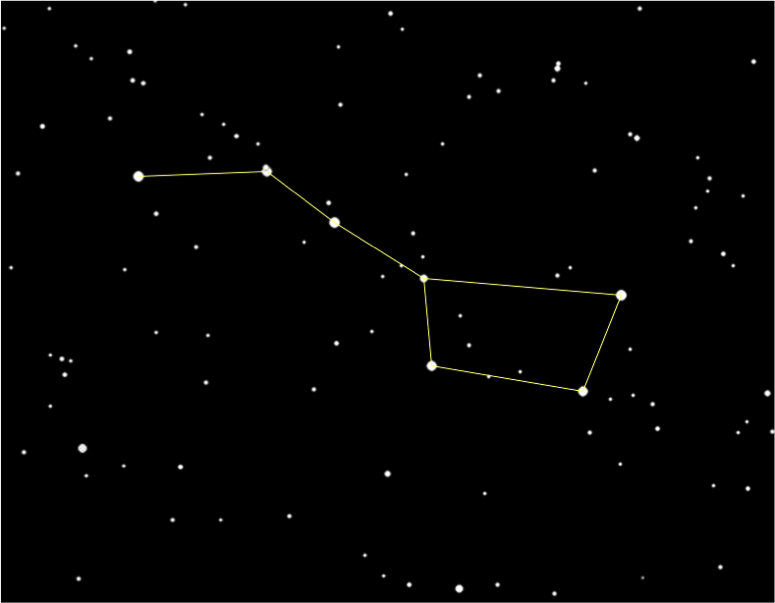
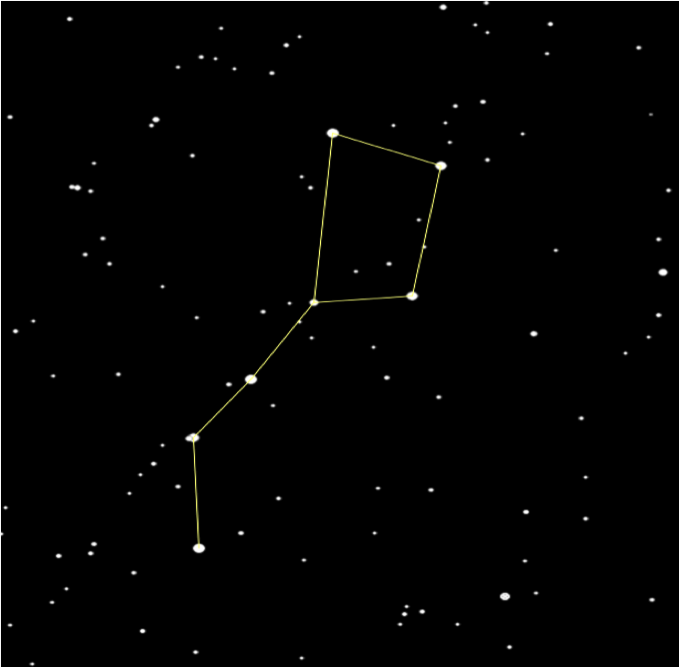
Back to Constellations
By now we should know that constellations appear to move across the night sky throughout the night, because the Earth is spinning on it's axis.
From left to right a constellation may look like this throughout the night at 9:00 pm, 12:00 am, 3:00 am, and 6:00 am.
Let me blow you're mind! This also happens throughout the year too!
The position of a constellation will change throughout the seasons, but you have to observe that constellation at the same time of night (ex. 12:00 am).
From left to right a constellation may look like this throughout the seasons at the same time of night.
This happens because Earth not only spins on it's axis, it also orbits around the Sun. Kind of a double spin, enough to make your head spin!