What Happens When Air Gets Hot?
We know that air is made up of tiny particles called atoms, and atoms are constantly bouncing around in the space they occupy.
When air is heated many things happen:
- the tiny particles in the air becoming energized
- they begin bouncing around much more
- the air becomes less dense
- less dense air rises
The reason why we have wind, weather, rain, tornadoes, gliders, hot air balloons, and mirages is because hot air is more buoyant than cold air.
Air Buoyancy:
The ability of an object to float or rise when placed in a fluid.
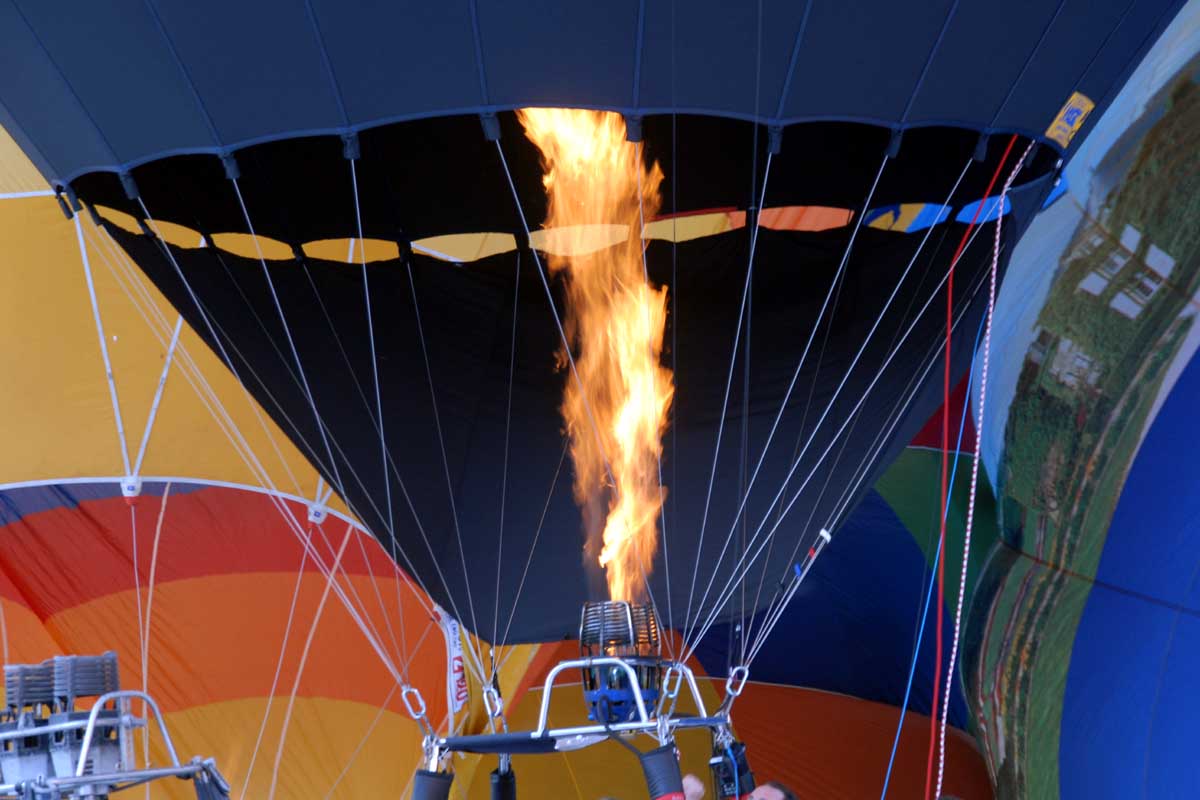
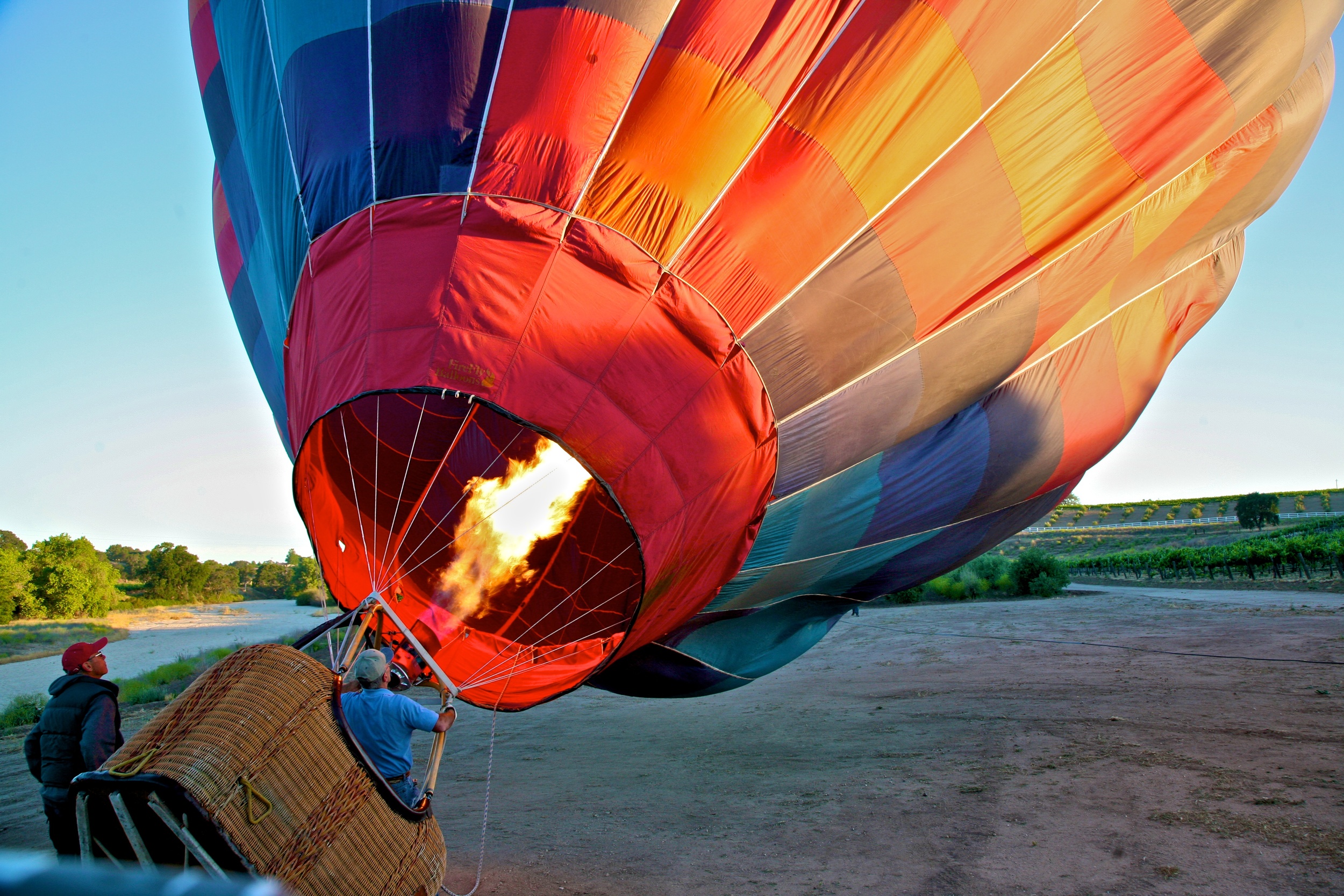
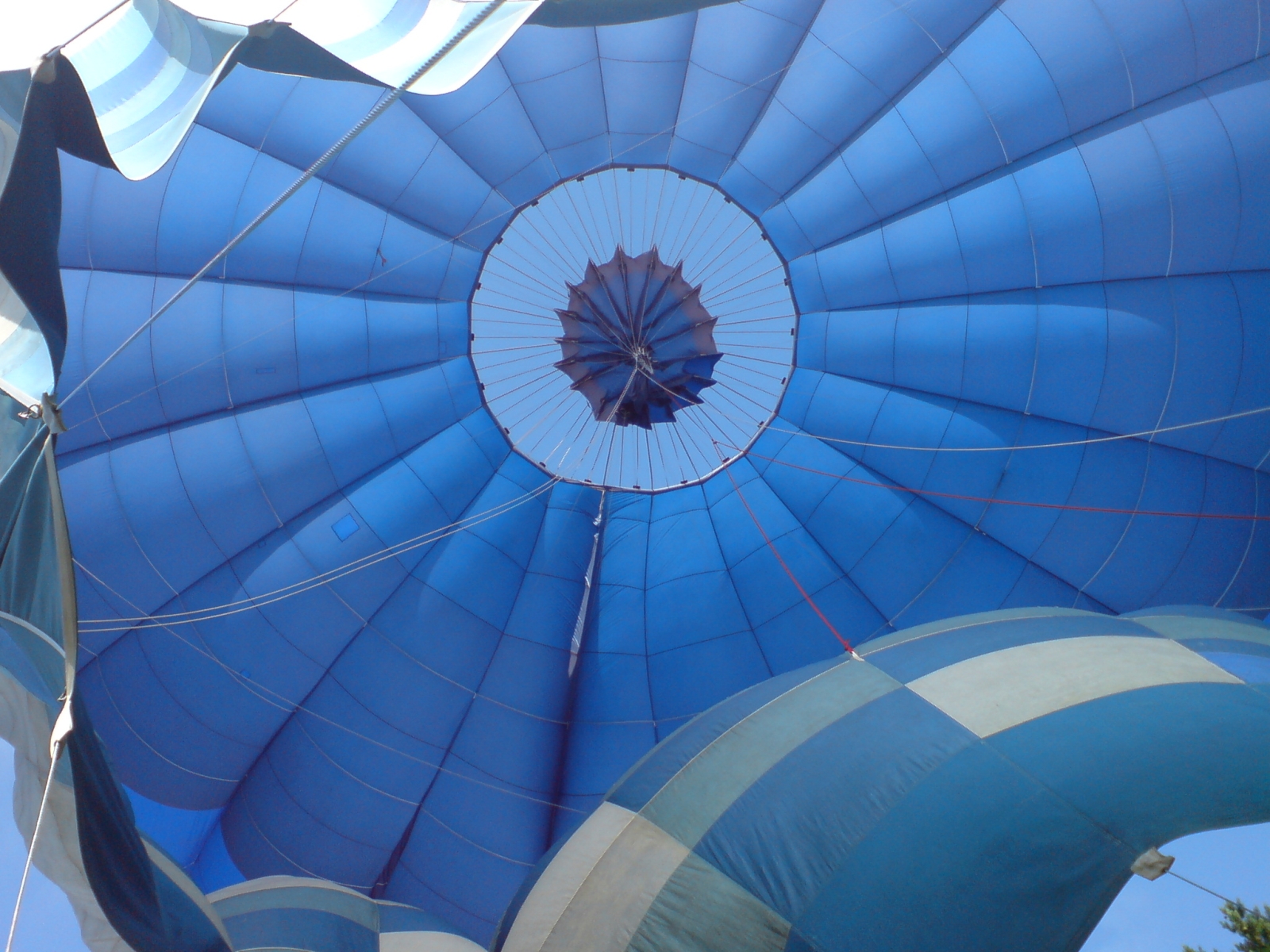
How do Hot Air Balloons work?
Hot air balloons work on the same principle of buoyancy to achieve flight!
Since hot air is lighter than cool air, it is less dense. A hot air balloon rises because it is filled with hot air, weighing less than the cooler dense air that surrounds it.
A hot-air balloon has three essential parts:
- The burner, which heats the air
- The basket, which carries the passengers
- The balloon envelope, which holds the air
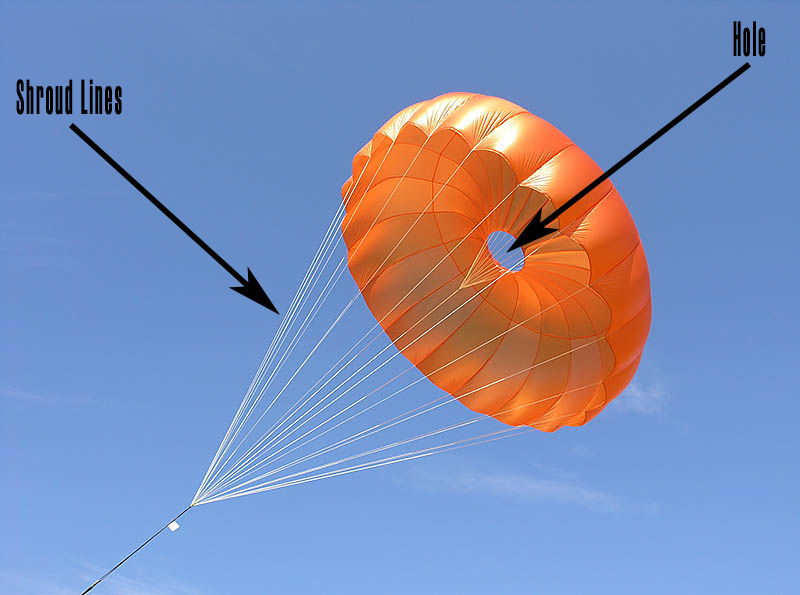
Parachutes!
Shroud lines:
Connect the weight to the parachute
Hole:
The hole on top of the parachute is to increase stability of the parachute
Control Surfaces
An aircraft is made up of several different parts that enable a pilot to have a successful flight.
Ailerons:
- Hinged flaps on the trailing edge of an aircraft's main wing are called ailerons
- Changes the amount of lift of a plane
- Used to make the airplane bank left or right, which is called roll.
If the left aileron is raised and the right one lowered, the air moving over the upper surface of the left wing is slowed, thereby increasing the air pressure. As a result, the plane banks to the left.
Elevator:
- Two smaller flaps on the small wing of the plane's tail (horizontal stabilizer)
- Elevators are used to control pitch. Pitch is the upward or downward movement of the plane's nose.
With the elevators down, lift on the tail is increased and the nose drops. With the elevators up, lift on the nose is increased; the tail goes down and the nose rises.
Rudder:
- The flap attached to the tail of the wing on the vertical stabilizer.
- The rudder moves the nose of the plane from left to right, this is called yaw.
If the rudder is turned to the left, the nose of the plane turns left. If the rudder is turned to the right, the nose of the plane turns right. Pilots use both the ailerons and the rudder to turn the plane.
How Helicopters Work
One of the problems with most aircraft is that they are quite large and cannot hover in one place. They must be moving forward all the time in order to achieve lift. Tadah! Helicopters!
Helicopters are designed with:
- A giant horizontal propeller known as the main rotor , which spins around very quickly
- A smaller vertical propeller known as the tail rotor, which counters the spin of the main rotor
Each of the long thin blades of the rotor is the shape of an airfoil . These blades cut through the air at high speeds and provide the helicopter with lift.
If the pilot wants to move the helicopter in a certain direction, they tilt the main rotor in that direction.
Aircraft VS. Spacecraft
There are two major differences that affect the design of aircraft and spacecraft:
- Gravity
- Atmosphere
Without air in space the Bernoulli principle does not apply, and with very low gravitational forces the space craft can maneuver using small jets instead of control surfaces.